
: Admin : 2022-06-10
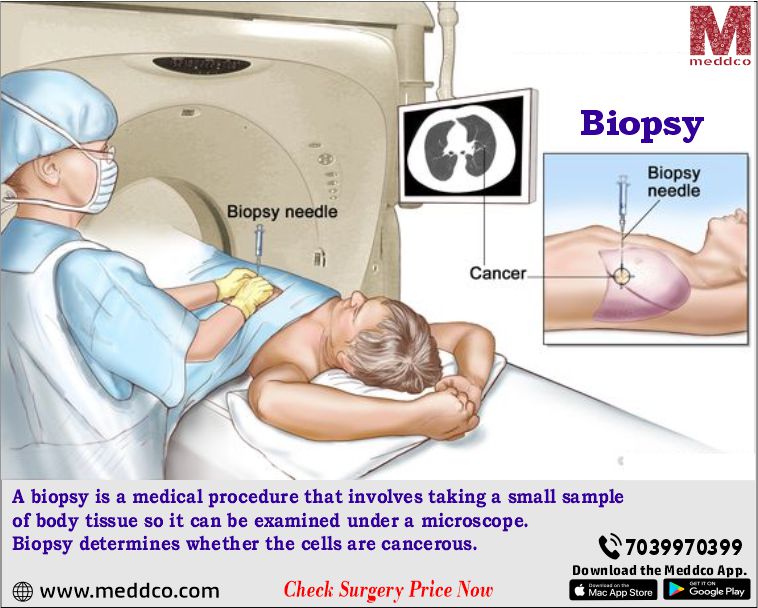
What is a biopsy?
The biopsy is a surgical procedure in which a small tissue sample removes from any abnormality or suspicion section for microscopic examination and further detection of the presence or absence of any cancerous cells. That small tissue sample can be taken from any body part, including the skin, stomach, kidneys, liver, lungs, etc.
Types of biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy is generally used to diagnose a spread of blood problems, each cancerous and not cancerous. If your doctor suspects problems with the patient blood, they suggest a bone marrow biopsy. This biopsy is also used to analyze whether cancer cells are from another body part and have spread to bones.
Endoscopic biopsy – in this biopsy surgeon takes tissue samples from the intestines, colon, lungs, and bladder. The Surgeon uses an endoscope to gather tissue samples. An endoscope is a thin, long, optical tube with a light-on-end instrument to see deep inside the body.
Skin biopsy – A skin biopsy is mainly used to examine skin conditions, including melanoma and other cancers. There are different sorts of skin biopsies (shave, punch). The sort of skin biopsy a patient go through depends on the sort of cancer suspected and the number of suspicious cells.
Surgical biopsy – The Surgeon may additionally suggest a surgical biopsy if the cells can't be accessed with different biopsy strategies or if other biopsy consequences have been unsettled.
Who is a pathologist?
A medical healthcare provider who treats or examines fluids, body tissues, or organs taken from the patient body. He/she is likewise responsible for performing lab checks.
A pathologist enables other healthcare vendors to attain diagnoses and is an essential treatment group member. Pathologists frequently work with a surgically eliminated sample of diseased tissue, known as a biopsy. The pathological treatment of the whole body is called an autopsy.
Why need of biopsy?
The Surgeon recommended biopsy in such cases:
• Surgeon often recommends biopsy when they are not certain of the cause of the disease, or they do not understand how a long way it has spread or precisely what it is like.
• Biopsies are recommended mainly by surgeons to either verify or rule out suspicions of cancer.
• Biopsies also diagnose inflammatory disorders such as in the kidneys or livers, infections such as tuberculosis, and immune disorders.
• Biopsy is also performed if someone wants to transplant any organ to check if it is a correct match.
• Sometimes, a biopsy is done to decide your remedy plan. For example, a biopsy can also assist your Surgeon in deciding if surgery is the best treatment or if a different treatment can be taken into consideration instead.
Does ordering a biopsy mean a patient possibly has cancer?
Not always; just because the patient is having a biopsy doesn't mechanically imply he/she has cancer or any other particular condition. Even though biopsies are frequently ordered when there's suspicion of cancer, results frequently come back negative (you don't have cancer).
The Surgeon also ordered a biopsy for a patient health concern, opposite to cancer. A biopsy is simply like other tests. It's just another tool for surgeons that helps them understand what is happening inside the patient body.
Is biopsy painful?
If the Surgeon uses anesthesia, there ought to be no pain during the process, even though there may be a skin prick throughout the initial injection. A patient undergoing a needle biopsy would possibly experience a sharp pinch. Relying on the biopsy, there may be some discomfort on the incision or puncture sites for some days.
Is biopsy safe?
Biopsies are usually secure, low danger tactics. There's a risk of infection and bleeding, as with any skin disturbance. In rare instances, excessive bleeding can arise. This could require further tactics to be accurate.
A biopsy can assist doctors in offering an early analysis of cancer and other diseases, and, in many instances, early detection is fundamental to growing survival rates.
It is hard to consider that biopsies are overwhelmingly secure strategies that can provide essential data for a patient's future health.
How long does a biopsy take to heal?
The patient may feel pain for a brief time, no matter what biopsy he had. Patient recovery may depend on the biopsy, location, and size of biopsy, and what kind of anesthetic it involves, local or general. Healing times depend on patient conditions. If the Surgeon does stitches after a patient biopsy, it'll increase the healing time. The Surgeon recommends pain relievers, which will help the patient ease discomfort during heal.
When to call the doctor?
The patient should call their doctor immediately:
• If pains get worse time by time after biopsy.
• Having fever after biopsy is a sign of infection. Call your doctor if a patient has a temperature above 100.5 F for 24 hours.
• If the patient biopsy site doesn't stop bleeding, he should apply firm pressure over the site for 20 minutes. If the bleeding won't stop and persists, the patient should call his doctor.
• If the patient observes any redness, oozing, or swelling from the biopsy site, the patient better calls the doctor.
biopsy cancer bone marrow endoscopic biopsy skin biopsy
No Comments