
: Admin : 2021-12-29
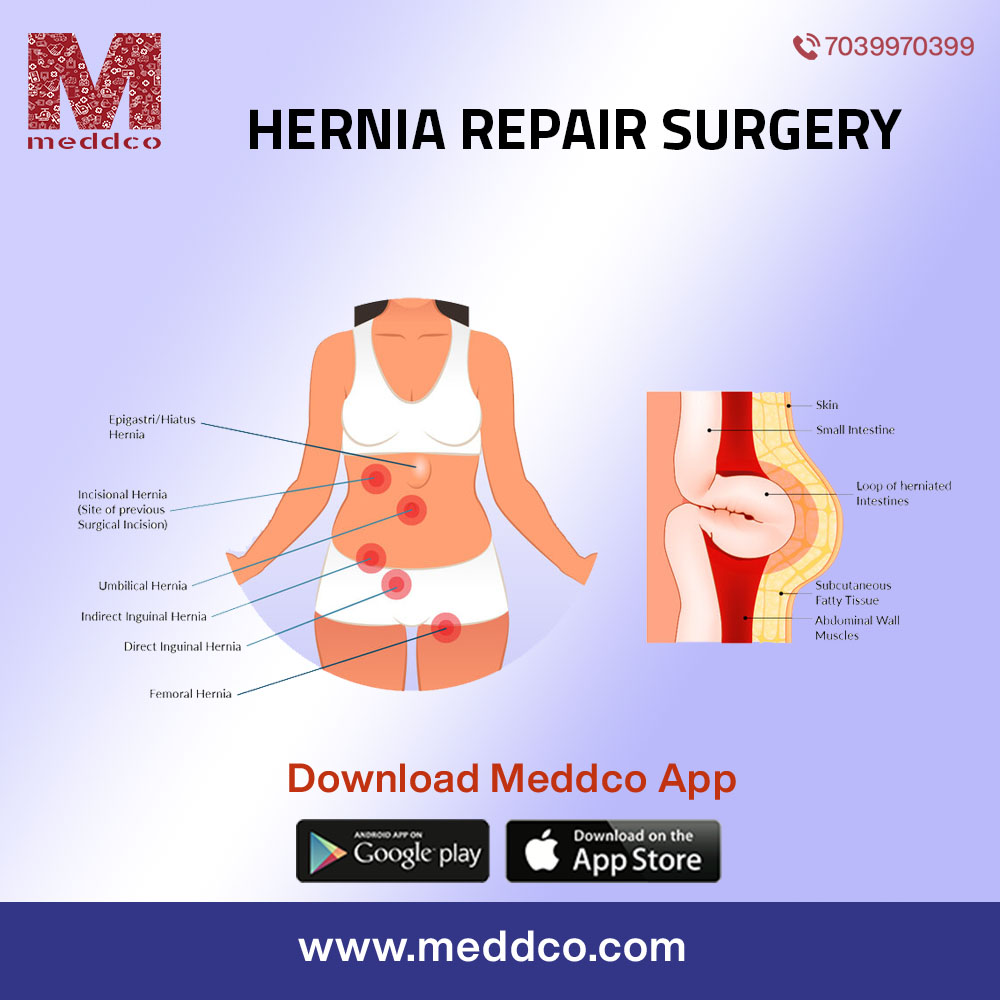
What exactly is a hernia?
A hernia develops when an internal organ or other bodily component protrudes through the muscle or tissue wall that typically holds it in place. The intestines, for example, may burst through a weakened spot in the abdominal wall. Hernias usually heal on their own, and surgery may be required to correct them. However, your doctor will advise you on the best treatment for your hernia and may send you to a surgeon. If the surgeon believes it is essential to repair your hernia, he or she will personalize the technique of treatment to your specific requirements.
An abdominal hernia arises when an organ or other piece of tissue protrudes through a weakness in one of the muscular walls enclosing the abdominal cavity. A hernia often manifests as a protrusion in the abdomen, upper thigh, belly button, or groin
What are the different types of hernia?
Inguinal hernia - The most common kind of hernia, occurring more often in males than in women. This is because, immediately after birth, a man's testicles descend down the inguinal canal, and the canal is meant to close almost completely behind them appears in the inner groin area (inguinal canal).
What causes hernias?
Ultimately, all hernias are formed by a combination of pressure and weakness or opening in muscle or fascia; the pressure drives an organ or tissue through the weakness or opening. Muscle weakness may develop from birth, although it is more common later in life. A hernia may be caused by anything that creates an increase in pressure with muscular weakness in the abdomen, such as:
Furthermore, obesity, poor diet, and smoking may all weaken muscles and increase the likelihood of hernias.
What is the prevalence of hernias?
Hernias are most common in people between the ages of 40 and 70. Normally, the male to female ratio is 7:1.
How is a hernia diagnosed?
Typically, a physical exam is all that is required to identify a hernia. Your doctor will examine the region for a bulge. Because standing and coughing may accentuate a hernia, you will most likely be asked to stand and cough or strain.
What are the signs and symptoms of a hernia?
There are three types of hernia symptoms, each of which is detailed below:
Hernia reducible
Irreversible hernia
Strangulated hernia
Indications for Hernia Surgery
The extent to which you need treatment is determined on the size of your hernia and the severity of your symptoms. Hernia treatment options include lifestyle modifications and medication.
Dietary adjustments may typically relieve the symptoms of a hiatal hernia, but they will not cure the hernia. Avoid large or heavy meals, avoid lying down or bending over after eating, and maintain a healthy body weight.
Medication- If you have a hiatal hernia, over-the-counter and prescription drugs that lower stomach acid may alleviate your pain and improve your symptoms. Antacids, H-2 receptor blockers, and proton pump inhibitors are examples of such medications.
Procedure for Hernia Surgery
Hernia surgery is often the only option for therapy. Open repair, laparoscopic (minimally invasive) repair, and robotic repair are the three basic forms of hernia surgery. Let us go through each sort of surgery in depth. Depending on the severity of the hernia, a patient has two surgical treatment choices. Each of them is discussed more below:
Open Hernia Repair
A person is given local anesthetic in the belly or spine to numb the region, general anesthesia to sedate or assist the person sleep, or a combination of the two during open hernia repair, also known as herniorrhaphy.
The surgeon next creates an incision in the groin, transfers the hernia back into the abdomen, and sutures the muscle wall together. An incision or cut in the groin is used during open hernia surgery. The hernia sac holding the protruding intestine is located. The hernia is subsequently pushed back into the abdomen and the abdominal wall is strengthened with stitches or synthetic mesh. Most patients are released after a few hours of surgery and may return to work within a few days. Strenuous activities and exercise are prohibited for four to six weeks after the procedure. Hernioplasty is a surgical procedure that reinforces the region of muscular weakness using a synthetic mesh or screen to offer extra support.
Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair
A laparoscopic (minimally invasive) hernia surgery involves inserting a laparoscope via a tiny incision. Other tiny incisions in the lower belly are used to implant the tools used to repair the hernia. This treatment (laparoscopic surgery) is normally conducted under general anesthesia, thus the patient's general health will be evaluated before the surgery. During this procedure, there is no or little discomfort.
The surgeon puts a laparoscope — a thin tube with a tiny video camera connected to one end – through numerous small incisions in the lower belly. The camera transmits a magnified picture from within the body to a display, allowing the surgeon to see the hernia and surrounding tissue up close. While watching the monitor, the surgeon meticulously repairs the hernia with synthetic mesh using equipment. The abdomen is inflated with a safe gas (carbon dioxide) to provide room for the surgeon to examine internal organs. The defect is subsequently reinforced using mesh, which strengthens the tissue and reinforces the abdominal wall. Following the surgery, the tiny abdominal incisions are closed using suture sutures, skin staplers, or surgical tape. The incisions are scarcely noticeable after a few months.
People who have laparoscopic surgery often have a quicker recovery period. However, if the hernia is really big or the client has undergone pelvic surgery, the doctor may decide that laparoscopic surgery is not the best choice. The majority of individuals endure discomfort after surgery and need pain medication. For many weeks, vigorous exertion and heavy lifting are prohibited. The doctor will determine when the patient is safe to return to work. Infants and children may sometimes have pain, although they normally return to regular activities within a few days.
Laparoscopic hernia surgery has many advantages, including three to four little scars rather than one bigger incision, reduced discomfort after surgery, a speedier return to work, a shorter recuperation period (days rather than weeks), and fewer infections.
Robotic Hernia Repair Surgery
Robotic hernia surgery, like laparoscopic hernia surgery, employs a laparoscope and is carried out in the same way (small incisions, a tiny camera, inflation of the abdomen, projecting the inside of the abdomen onto television screens).Robotic surgery varies from laparoscopic surgery in that the surgeon is sitting in the operating room at a console and controls the surgical tools from the console. While robotic surgery may be used to repair minor hernias or weak spots, it can also be utilized to rebuild the abdominal wall.
The use of a robot provides excellent three-dimensional pictures of the interior of the abdomen, which is one of the most significant differences between laparoscopic surgery and robotic surgery (vs. the two-dimensional images of laparoscopic surgery).
The following are some of the primary benefits of Robotic Hernia Surgery over Laparoscopic or Open Hernia Surgery:
hernia herniasuregry abdomin inguinal hernia
No Comments