
: Admin : 2022-02-02
What is a Parotid gland?
The parotid gland is one of the major and largest salivary glands. The parotid gland is the salivary gland located below either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. The primary function of the gland is to create saliva. Saliva has numerous functions in the mouth. It is basically a hypotonic solution created by a joint effort of all the salivary glands. Saliva contains electrolytes, macromolecules and enzymes.
The parotid glands are considered the largest of the three pairs of major salivary glands. Saliva is an essential liquid present in the mouth. When human eats, saliva breaks down the food and helps to move down the throat. The parotid glands along with other salivary glands develop early. There are two lobes of the parotid gland which are separated by the facial nerve or cranial nerve VII. While surgery, the location of the parotid gland is essential as the facial nerve supplies signals that control the eyes and movement of the mouth.
What are the functions of the parotid gland?
The most essential function of the parotid gland is the creation of saliva. Saliva itself has several usages as it provides lubrication for the mouth. Saliva also assists in chewing, swallowing, digesting and even speaking. The parotid gland releases saliva which prevents infection in the mouth and also dental cavities. If a parotid gland stops working, the production of saliva will decrease and would cause a lot of problems.
Where does the parotid gland lie in the human body?
The parotid gland generally lies in front and below the earlobe. The parotid gland generally produces saliva inside the mouth. The saliva then drains from the gland through a tube that opens on the inside of the cheek that is opposite the upper back teeth.
What are the signs and symptoms of a Parotid Tumor?
The major salivary glands are on each side of the mouth present below the tongue. Several others nerves and structures run through or near the salivary glands and can be affected by salivary tumours. The possible signs and symptoms of the tumour are:
If Facial nerve damage occurs, it may result in facial muscle twitching, weakness, or paralysis. The signs and symptoms of facial nerve damage are a bit different than that of parotid tumours. They are:
What is Parotidectomy?
A parotidectomy is the removal of the parotid gland. Parotidectomy is one when a lump is formed inside. The parotid gland has two lobes. One is the superficial lobe and the other is the deep lobe. The removal of the parotid gland is mainly done when tumours are found in the gland. Surgery is performed carefully as the facial nerve is nearby. If the surgery is not performed carefully, it can affect the facial nerve that controls our ability to close eyes, raise eyebrows, and smile. Therefore, preserving the facial nerve is important when removing a parotid gland tumour.
The types of Parotidectomy are:
Superficial Parotidectomy
The surgery to remove a tumour in the superficial lobe is called a superficial parotidectomy. Doctors recommend superficial parotidectomy or surgery to remove all of the superficial lobes when the tumour is only restricted to the superficial lobe of the parotid gland. The surgery is done to remove the tumour that begins at the front of the ear and follows the line down to the neck and under and along the jawline.
Total Parotidectomy
The surgery to remove a tumour in the deep lobe or even in the superficial lobe is called a total parotidectomy. Doctors recommend a total parotidectomy or surgery to remove the deep lobe, when the tumour is restricted to the deep lobe or if the cancer is located in both the deep lobe and the superficial lobe. The procedure of the surgery is the same as superficial parotidectomy.
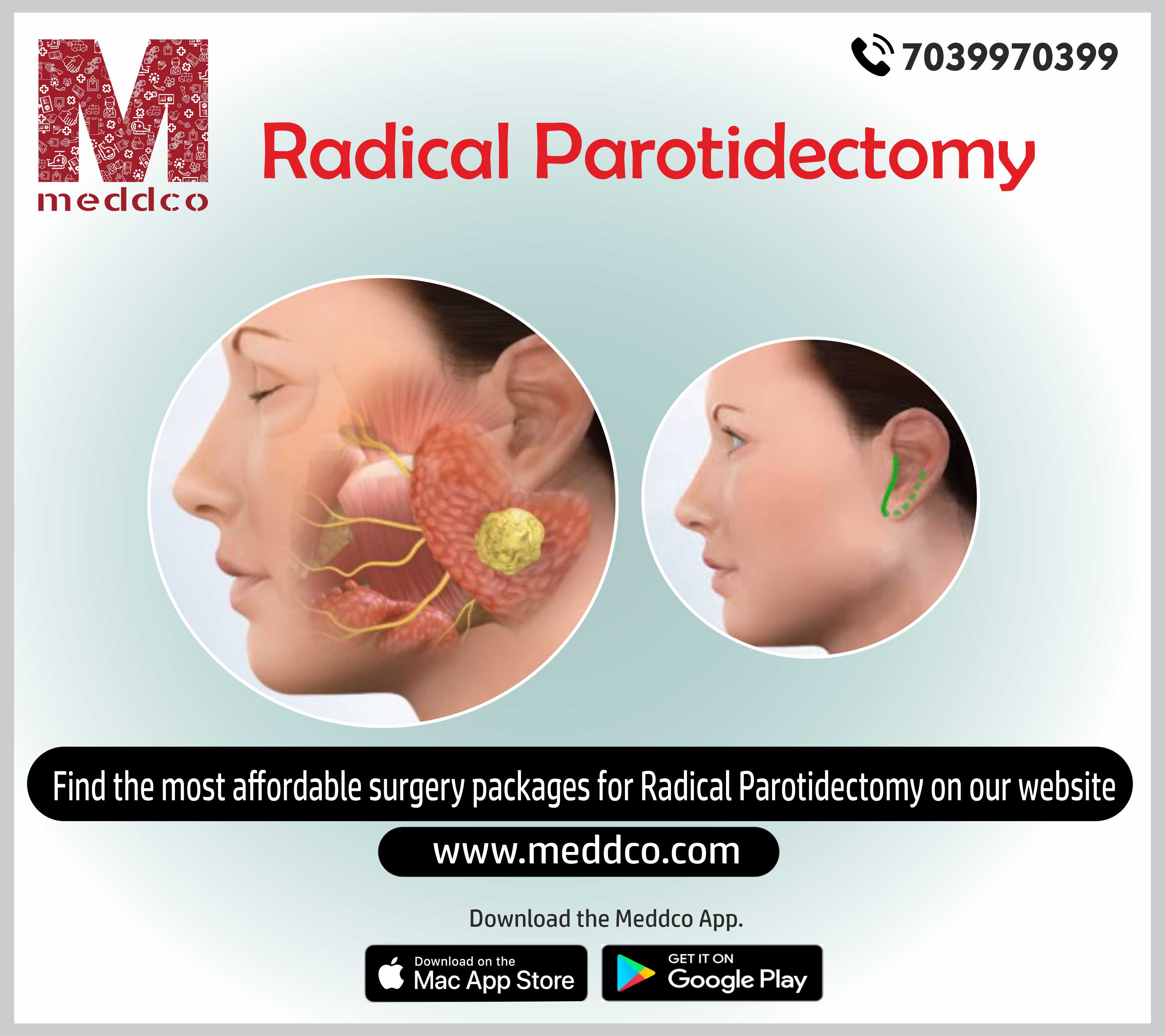
Radical Parotidectomy
Radical Parotidectomy is performed if malignant neoplasm is impinging on facial nerve. Facial nerve is surgically operation in addition to parotid gland.
Extracapsular Dissection
Extracapsular Dissection is the surgery of the parotid tumor surrounded by some millimetres of healthy tissue. It is done without searching and exposing the main line of the facial nerve.
What is Radical Parotidectomy?
Radical parotidectomy involves the removal of all parotid tissue and also the facial nerve. Radical Parotidectomy is done where the facial nerve has been invaded by a tumour or if preoperative facial nerve function is impaired in the presence of malignant disease.
How should the patient prepare before Operation?
Many measures before a parotidectomy are performed before surgery. Doctors check the medications and performs some tests prior surgery. Some of these include diagnostic imaging, fine-needle aspiration, neck dissection, and antibiotic prophylaxis. Diagnostic imaging is a scan or MRI is done to locate the tumour and address the complications. Fine-needle aspiration is a technique performed to help the surgeon physically diagnose the malignancy of the tumour. Neck dissection is another technique only considered in the most extreme of cases before a parotidectomy.
How is radical Parotidectomy performed?
Radical Parotidectomy is removing the facial nerve. The nerve is being grafted through the nerve-grafting technique. The surgeon carefully operates the damaged intra-temporal facial nerve, which controls lip and mouth movements. Below it lies the hypoglossal nerve, which controls the tongue. The surgeon grafts the paralyzed nerves to the healthy nerves using tiny sutures.
What is the surgical procedure for other Parotidectomy?
The treatment of the tumour involves surgery. Through a surgical procedure, the tumour is removed. But if the tumour contains cancer cells, the surgeon refers to treatments like radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
Operation of the parotid gland is removing the tumour without harming the healthy parotid gland tissue around it. This is called superficial parotidectomy. In some cases, the parotid gland is removed totally. This is called total parotidectomy.
Extensive surgery is done for cancers. If parotid cancer has grown near the bone and muscles, it may be necessary. Surgeons try to remove all of cancer and a small amount of the healthy tissue that surrounds it. Then they work on repairing the area so the patient can continue to chew, swallow, speak, breathe and move his/her face. This may involve transferring or grafting skin, tissue, bone or nerves from other parts of the body to make repairs.
Surgeons make an incision near the ear to access the parotid gland. The facial nerve is taken care of as it controls facial movement, so stretching or cutting the nerve can cause partial or complete paralysis of the face that can be temporary or permanent.
Radiation therapy is used to kill cancer cells. Powerful beams are used to treat the cancerous parotid tumour. Radiation therapy is used as an initial treatment when surgery isn't an option.
Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses medications to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy is not used to treat parotid tumours. But in some cases, it is combined with radiation therapy to treat parotid cancers that have a high risk of spreading or the ones that can’t be removed. Chemotherapy is an option for people with advanced parotid cancers that have spread to other parts of the body.
What should a patient do Post Operation?
After completion of a parotidectomy, patients can expect hospitalization for up to one week. Patients are administered and antibiotics are provided to minimize the risk of infection as well as an assessment of pain management is done throughout their stay. The stay of hospitalization changes from patient to patient. Most patients are being discharged within 24 hours after surgery. If a tumour is malignant, many patients are referred to radiation therapy too.
Can facial nerve damage be repaired after radical parotidectomy?
The facial nerve is the most sensitive part and, in some cases, it is repaired on its own. Damage caused by trauma can be repaired. Patients ideally recover within the first 4 weeks. Complete recovery might take up to 6 months.
There are also surgical methods to repair facial nerve damage. Those are:
What are the risks of having a parotidectomy?
The surgery can have many risks and side effects. They are:
How does the recovery work after surgery?
The recovery from a parotidectomy will depend on the extent, type and procedure of surgery the patient has had. Surgeons are generally notified about surgical incisions or drains after leaving the hospital. Medications are discussed and post-surgery symptoms are taken care of. The patient should go for complete rest and follow as per it is instructed. The patient should:
What are the possible side effects after Parotidectomy?
Post-Parotidectomy effects can be a bit complicated. The patient might feel tired or pain in the area. The complication rate is generally low and not much problem occurs after the surgery. However, it is essential to know about the side effects one might face.
The normal side effect after the surgery can be:
A patient might feel abnormal side effects after the surgery. Patients should immediately contact their physician if they experience any of the abnormal side effects of surgery.
These can be:
If a patient is confused about any side effects, they should discuss the same, go for check-ups and inform their doctor as soon as possible.
What Might Be The Prognosis Of Parotidectomy?
Post operation, there is a 50% risk of facial weakness directly. 1-2% of risk of permanent weakness might be there. Frey’s syndrome may occur in up to 90% of patients. The risk of mortality is very low after the surgery. Survival rates due to malignancy depends on the patient’s history of the disease. survival ratio for Parotid tumors account for 7% of all the cancers.
cancer tumor parotid parotid gland Parotidectomy
No Comments