
: Admin : 2022-06-18
What is Maxilla?
Our jaw is formed by the bone that's the Maxilla. The irregular right and left halves of the Maxilla bone fuse together within the middle of the skull that's below the nose, which is thought to be because of the suture
The Maxilla has many main functions that are holding the best teeth in place while making the Anatomically the Maxilla is that the original detailed and delicate structure of the face, any sudden trauma thanks to some violence, accidents due to vehicles, falls, gunshot wounds, industrial accidents end in major maxillary fractures. Fractures are forms of patterns and structures in faces, and their diagnosis and treatment become pretty challenging for the maxillofacial surgeon. Maxilla makes the essential component of the center third of the facial skeleton. The Maxilla may be a prominent bone within the midface because it is closely connected with adjacent bones that may provide structural support between the cranial base and the occlusal plane. As seen, the fractures of the Maxilla are less frequent than those of the mandible or nose due to their strong structural support. This bone is structurally strong, protecting the globes and brain, projection of the midface, and support for occlusion.
Depending on your injuries, the doctor will recommend surgical repair in line with the surgery needed. Details of the surgery needed, the procedure involved, recovery time, etc. They are going to be described by the doctors themselves.
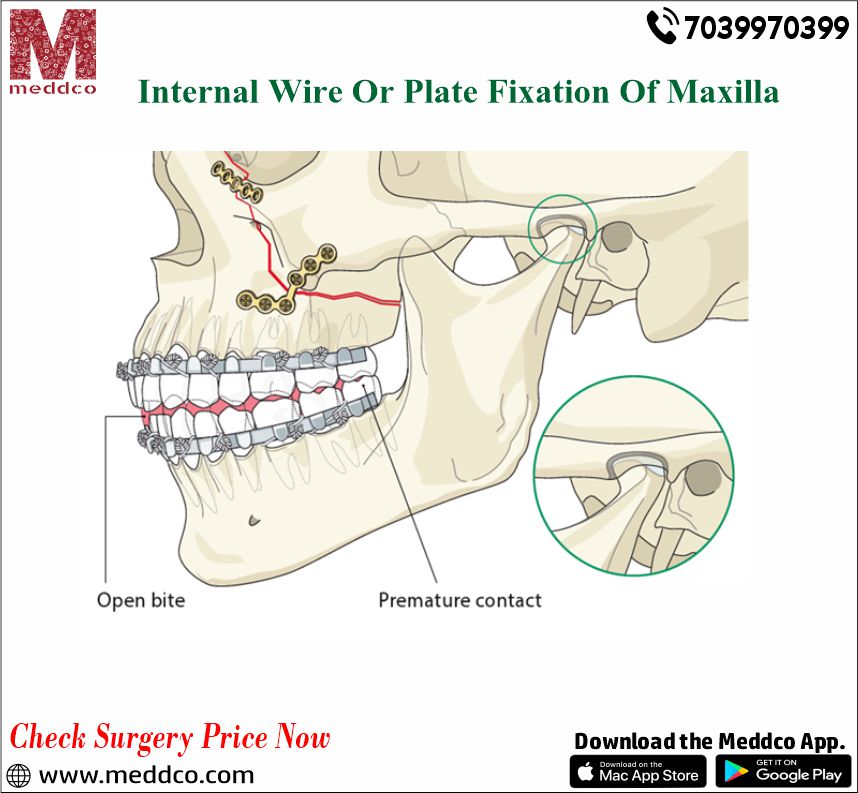
Internal fixation of facial fracture has the multiple challenges of restoring the face anatomy and functions impaired by the displacement of the fracture segments and avoiding the treatment-related complications. Internal wire fixation ensures alignment and gets in touch with the fracture fragments.
Fixation of Maxilla.
There can be many reasons; your Maxilla can get displaced or broken. Due to the displacement of the Facial fractures, stable fixation is required. This is done by internal fixation. The gold standard and widely used method in the modern era is the Plates and screws technology. However, wire osteosynthesis is still widely used due to the lack of resources.
Developing countries use wires widely for facial fracture internal fixation because it is effective and has fewer complications. Because the plating technology cost is high and not easily affordable, internal wire fixation is an affordable alternative for surgery.
The fractured fragments are fixed and immobilized in their anatomically reduced position by wires placed around teeth, referred to as interdental wiring.
There are multiple challenges in Internal fixation of facial fracture in restoring the face anatomy, as the fracture displacement impairs the functions. If someone avoids the treatment, then it can lead to related complications. Internal wire fixation ensures that the fracture fragments' alignment and contact are done properly.
One of the most economical methods is Transosseous wiring osteosynthesis of internal fixation as wire and arch bars are more easily affordable than plates and screws. Also, there's no need for a calibrated drill. The wire may be tolerated well and doesn't require removal. However, it's better than plates and screws; its disadvantages include the fact that it's not strong enough to stop inter-fragmentary motion across the fracture and lack directional control. When jaw fixation is required for stability within the mandibular or Le Fort fracture treatment, it should result in weight loss because feeding would be painful and lose feeding. Speech difficulty will affect the person's social life. The bone non-union may result because of a lack of stability. Passing the wire may risk iatrogenic bone substance loss, particularly on the jaw bones.
After the fracture, the surgery is performed within 6-10 days. The patient will be given local anesthesia. A soft stainless steel wire of 0.5mm-diameter was used for the fixation.
The transosseous wiring makes the jaws immobilized in mandibular or Le fort fracture patients. The patient is recommended for immobilization for six weeks in adults and three weeks in children. Antibiotics are provided and are continued for 7 to 10 days after surgery. Anti-inflammatory steroids are given for three days preoperatively and continued for 3 to 4 days postoperatively. For rinsing of the month, Chlorhexidine is employed. Diet usually are recommended which are liquidy and soft.
After the surgery, the complications of facial fracture are broad and include occlusion, mouth opening, vision, face sensory and bone union impairments, infections, and facial asymmetry. These complications can be resolved by the suggestions of doctors as well.
Many fixation methods are used with great success for the fixation of maxilla fractures. The internal focus is distributed with the assistance of mini plates, microplates, 3D plates, and reconstruction plates. Plating systems and wiring techniques help with maxillofacial fracture surgery and have a high success rate.
maxilla fixation of maxilla jaw lower jaw surgery maxillary fracture
No Comments