
: Admin : 2022-01-24
What are genetic defects that develop during birth?
The birth of a child is a dynamic complex physiological process. When sperm and ovum unite a zygote is formed. The zygote contains 46 chromosomes—genetic information, getting 23 from the male sperm cell and the rest 23 from the female egg cell. The fertilized zygote develops gradually within the uterus into a foetus. The zygote divides through the process of cell multiplication, called mitosis. Mitosis is a form of cell division in which each cell doubles – one cell becomes two, two cells unite to form four to develop into organ and organ systems. As the zygote matures into a foetus, several factors influence the process of growth, multiplication of cells into organ and organ systems. A foetus who inherits characteristics from the sperm cell and egg cells may be born with chromosomal abnormalities, genetic predisposition to certain diseases and birth defects.
Each haploid cell, male gamete and female ovum contain half the number of chromosomes. A zygote formed after a sperm cell fertilizes the ovum has 23 chromosomes from the male parent and 23 from the female parent cell. As the zygote matures to grow into a foetus, within the womb of the mother, it inherits characteristics or genetic traits from both parents. The genetic information is passed through the chromosomes into the offspring. So children look similar, have habits and virtues according to their parents. Children from an educated family become qualified professionals while most from an underprivileged community are labourers. Genetic factors play a role in the development of a child with socio-economic and cultural elements. Genetic mutations over a period of time cause different changes that contribute to the development and growth of a child.
Researchers have proved that several diseases, birth defects and metabolic syndromes are hereditary. They are passed on through generations, if a parent suffers from leucoderma, vitiligo—a skin disease or thalassemia-an inherited blood disorder where healthy haemoglobin is not produced to carry oxygen to different parts of the body—then a child is born with genetic or chromosomal abnormalities that cause these conditions to develop within him. Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, haemophilia, Down syndrome and sickle cell anaemia are a few other diseases that a patient inherits from parents, siblings or gets transferred through genetic mutations.
Congenital anomalies or birth defects cannot be linked to a specific cause. Certain reasons have been identified that are responsible for development defects in children. Defects in a single gene, chromosomal disorders, multifactorial inheritance, environmental factors, nutritional deficiencies, mother having gestational diabetes or those who consume alcohol, drugs, unnecessary medication and smoke during pregnancy can also cause congenital anomalies. Mutations in genes cause these defects. A child born with an anomaly suffers from severe troubles, observed in different clinical conditions. Babies born with cleft palate have difficulties during breastfeeding. A child born with Hemophilia- which is a bleeding disorder suffer from uncontrolled bleeding from low levels of blood clotting factors. A child born with an attention deficit syndrome inherited as an autosomal dominant trait from parents, suffer from aggressive, irritable impulsive hyperactive behaviour and difficulty while focusing at work.
What is tongue-tie or ankyloglossia?
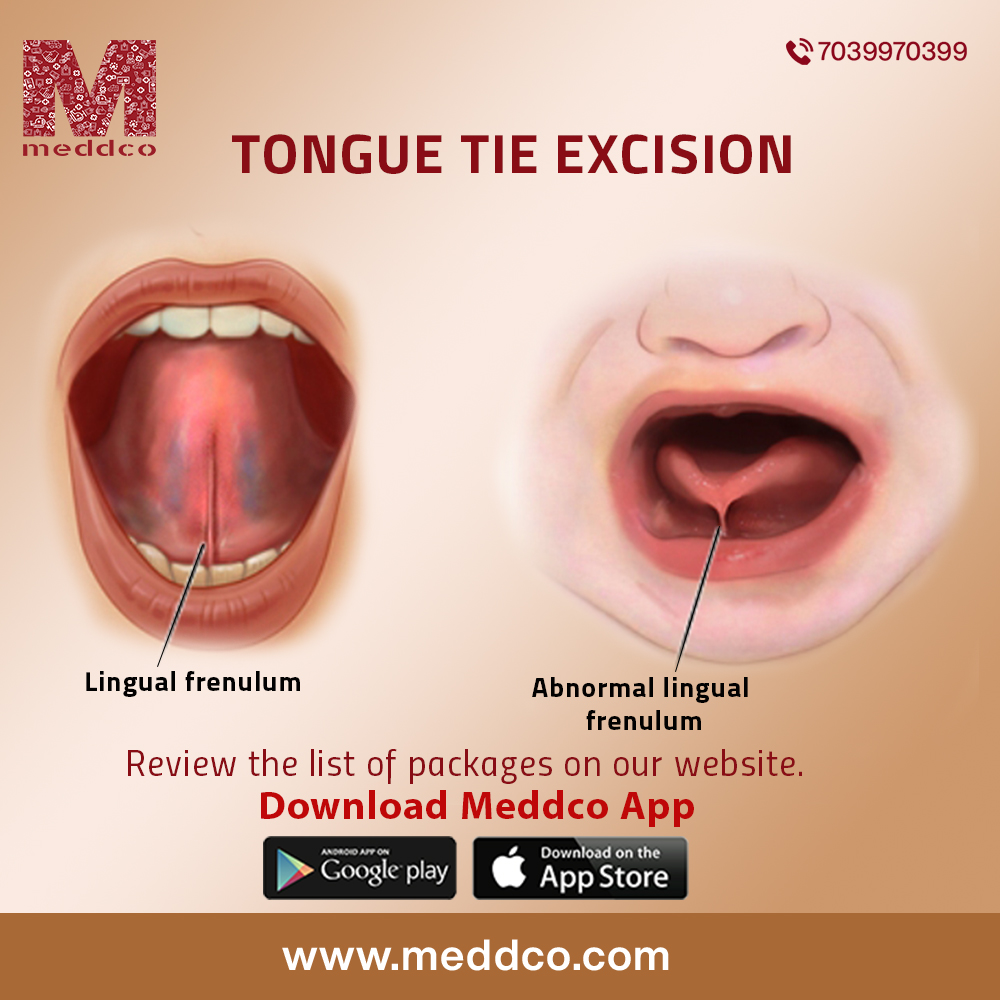
A metaphor is often used for children as being tongue-tied for those who have difficulty while speaking, may have stammering speech and problems during dentition. A frenulum is a small ribbon-like tissue that extends from the floor of the mouth to the bottom of the tongue. Ankyloglossia is a congenital anomaly in which a baby is born with a short thick frenulum that restricts normal tongue movement. The tongue remains attached to the floor of the mouth in a patient having ankyloglossia, restricting its movement. It is more common in male children. It develops when the child is developing inside the womb of the mother. It has been found that it is an X linked cleft palate syndrome. Genetic mutation of the MTHFR gene is responsible to cause this birth defect. This defect is hereditary, with the incidence of 10% of infants and children born with this anomaly.
An embryo within the womb of the mother grows through cell multiplication to form organ and organ systems. The fusion and development of most structures take place during the first and second trimesters of pregnancy. The tongue and floor of the mouth fuse together when the foetus is developing inside the womb of the mother. Later the tongue separates from the floor of the mouth. A small cord connects the bottom of the tongue to the floor of the mouth. As the child grows, this cord of tissue becomes thin and shrinks. In children affected with tongue-tie, this band of tissue does not become thin nor recede, so the movement of the tongue which should ideally be flexible becomes restricted, making speech and feeding difficult.
Ankyloglossia can be classified into four types—
Type I – The band of skin or frenulum is thin and elastic which gets attached to the tip of the tongue to the ridge behind lower teeth.
Type II – The tissue or frenulum is fine and elastic while the tongue gets adhered 2 to 4 millimetres from the tip to the floor of the mouth close to a ridge behind lower teeth.
Type III – The band or frenulum is thick, stiff and adheres to the tongue from the middle of the underside of the floor of the mouth.
Type IV – The frenulum lies posterior, invisible but thick fibres can be felt by the physician adhering near the floor of the mouth.
The above group and classification help to decide the treatment. After a thorough examination by a skilled, experienced physician the surgical treatment is decided to be performed on the child to relieve him from symptoms of tongue-tie birth defect condition.
What are the symptoms of ankyloglossia?
A child passes through developmental milestones in life. A child is breastfed after a few minutes of his birth. The impulse to suck milk naturally from the mother's mammary gland is an involuntary autonomic reflex response that evolves in a newborn infant. As he grows, speech and different motor skills develop. A discomfort, a congenital defect or a handicap that cause fundamental obstacles in accomplishing different milestones may adversely affect his health. The problems a child suffers when he has ankyloglossia begins right from the initial step of breastfeeding to talking or speech genesis. Symptoms range from mild to severe. Due to the frenulum or the banded tissue, the tongue appears to have a notch that affects daily life activities.
A baby finds it difficult to swallow or gulp milk during breastfeeding.
Baby feels a constant hunger as he has to put increased effort while sucking milk. So every time an incomplete act leaves the child half-starved which forces him to frequent desire to ask for more milk at short intervals.
An insatiable, never full sensation leaves the child famished, with loss of weight.
When a child grows up to two years of age without treatment of this condition, then he develops speech impairment. A tongue needs to contact the roof of the mouth while pronouncing certain sounds which becomes painstakingly difficult or troublesome due to restricted movements of the tongue.
Difficultly while licking any creamy food products.
Swallowing food and liquids is difficult for growing children.
If the child experiences the above symptoms he requires medical attention. A paediatrician can identify this clinical condition by examining the floor of the mouth.
What is tongue-tie excision?
A patient who is diagnosed with tongue-tie needs surgical treatment termed as tongue-tie excision—frenotomy and frenuloplasty. When symptoms are severe, an infant, a toddler or an adult may require this surgical treatment procedure.
Parents should be aware of the severity of their child suffering from this congenital anomaly. They should know treatment options, risks involved during the surgery, whether anaesthesia would be administered and the benefits of the surgical procedure.
FRENOTOMY – It is a common, simple surgical procedure done with or without anaesthesia in an outpatient clinic or hospital. Nerves and blood vessels surrounding the cord or band of tissue called frenulum are less, so when the frenulum is excised using sterile scissors, it causes minimum discomfort to the patient. Complications post-surgery are rare. Baby is now can breastfeed for a prolonged comfortable period by easy, swallowing milk and fluids.
FRENULOPLASTY – When the frenulum is too thick, a more extensive detailed procedure is needed for the repair of the tissue. General anaesthesia is given to the child prior to this procedure. The frenulum is excised with the help of surgical tools, the cut is sutured to close the wound. These sutures get absorbed within buccal mucosa as the tongue heals. Complications of this treatment procedure are rare.
LASER surgical treatment is an advanced technique, considered better than the conventional surgical options. Cauterisation of the tissue has fewer complications as additional sutures are not required. The frenulum incision is done using a diode laser using a definite wavelength as power is applied at the centre of the frenulum from the tip to the base of the tongue. Laser treatment is a safe alternative method for children that causes minimum infection, swelling and bleeding. All the above surgical treatment procedures are done by skilled health care professionals.
Patients are later advised to consult a speech therapist for articulation, improvement of speech.
A tongue-tie excision may have few advantages over certain complications. However, the risk of these complications has to be taken care of with utmost caution to prevent damage to the buccal cavity.
Tongue-tie excision improves breastfeeding problems. A child will be able to feed better through increased sucking impulse, gulp the milk easily thereby improving his digestion which will cause weight gain. As surgery solves the problem of feeding in children, it prevents the problem of nipple pain in nursing mothers. A child post-surgery does not suffer from dental and speech problems.
One of the risks of this treatment procedure is, it may cause infection which can be avoided by taking necessary precautions by the treating physician.
Is tongue-tie excision common in adults?
Children who do not have severe symptoms due to tongue-tie, or just have a minor thin band of frenulum—a band of tissue that connects the floor of the mouth to the tip of the tongue, may not cause many problems during childhood. In such cases, it remains unnoticed or is left untreated as the child grows into an adult. The tongue tie conditions can cause problems in speech, playing a wind musical instrument through the mouth, eating, drinking and breathing problems, dental issues causing incorrect oral or dental hygiene. Adapting to tongue-tie in adulthood may cause sleep apnoea. It reduces the quality of life in patients.
Tongue-tie excision can be done in adulthood. A physician examines the condition, records symptoms, medical history of the patient, to plan the surgical treatment. It is best that the surgery is done at an early age but many times it is done when the child grows into a teenager.
FRENECTOMY is the surgical removal of the frenulum or band of tissue that causes several oral difficulties during adulthood. The surgery is done by giving general anaesthesia to the patient. Later the thin band or frenulum is excised, taking care that it does not cause any complications.
Once this clinical condition is treated, certain exercises prescribed by the doctor should be done by patients to improve speech. These exercises are also recommended in patients who do not wish to undergo a tongue tie excision. Exercises prescribed by the therapist may help a patient to cope with movements of the tongue that aid in speech through controlled adaptive skills while performing actions using tongue and mouth.
ORAL KINESTHESIA – It is an exercise to visualize the tongue and observe the pattern of its movements. The patient feels, senses these movements to gradually resolve problems from tongue tie or ankyloglossia.
DIADOCHOKINESIS – This exercise involves rapid, alternating movements of the tongue. While practising this exercise regularly, helps to increase muscle memory, which helps to adapt the tongue from minor obstacles and problems that the patient may experience due to ankyloglossia.
A tongue-tie condition is often neglected in childhood. Patients facing embarrassing situations, clinical symptoms and signs of problems while performing oral actions where the tongue is involved, during adulthood, needs surgical intervention. Alternative methods suggested by a therapist are supportive guides, hearing aids in the form of exercises, along with a tongue tie excision.
tongue tonguetie tongueexcision
No Comments