
: Admin : 2022-07-07
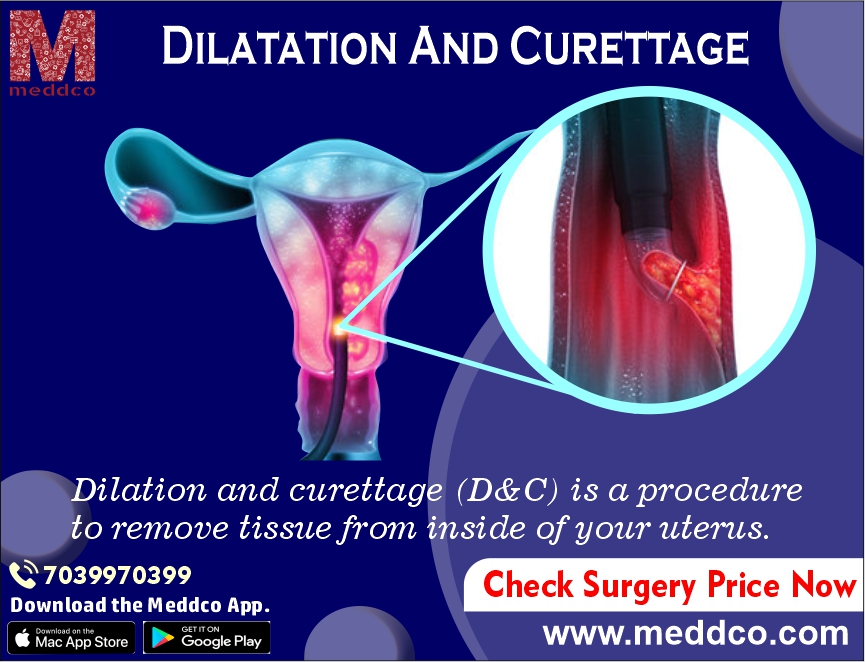
Dilation and curettage (D&C) is a surgical operation that removes material from the uterus. The term "dilatation" refers to the dilation (or opening) of the cervix, which is the bottom section of the uterus that opens into the vagina. The scraping or removal of tissue lining the uterine cavity (endometrium) using a curette is referred to as curettage.
A D&C surgery may be performed for a variety of reasons, including determining the origin of a condition, such as abnormal uterine bleeding; treating a miscarriage or postpregnancy hemorrhage; or performing a first trimester abortion (pregnancy termination).
WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR D&C
A D&C may be done for a variety of reasons. In certain circumstances, the surgery is performed to learn more about the uterus in order to detect a medical issue (called a diagnostic D&C). In other circumstances, the technique is utilized to address a medical disease or issue (called a therapeutic D&C).
Diagnostic D&C – The major purpose for a diagnostic D&C is to gather and evaluate endometrial samples (lining of the uterus). This may be done due to abnormal uterine bleeding, abnormal findings from a prior endometrial biopsy, test, or imaging scan, or, in rare situations, to screen for pregnancy tissue in a person who has an early abnormal pregnancy. In most situations, a health care professional will initially attempt to collect uterine tissue using an office procedure known as an endometrial biopsy. A D&C may be required if an endometrial biopsy is not feasible or if not enough tissue is recovered.
Diagnostic D&C is occasionally combined with hysteroscopy, which includes dilating the cervix and inserting a thin camera to view and image the interior of the uterus. The images are shown on a monitor, enabling the doctor to observe the endometrium up close. This allows the doctor to avoid missing any structural abnormalities (such as polyps or fibroids) within the uterus and to collect a sample from the most clearly aberrant places.
Following a diagnostic D&C, a pathologist analyzes the tissue under a microscope to look for endometrial polyps, precancer of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia), or endometrial (uterine) cancer.
Therapeutic D&C is performed to remove the contents of the uterine cavity in the following situations:
Miscarriage - In some miscarriages, the tissues of the pregnancy are totally passed. In certain circumstances, a D&C is required to remove this tissue or to assure that it has completely gone.
Abortion – A D&C is one way that a person might utilize to terminate (end) a pregnancy.
Molar pregnancy treatment – A molar pregnancy is an abnormal pregnancy in which a tumor arises in lieu of the normal placenta. The conventional therapy for molar pregnancy is D&C.
Retained pregnancy tissue — A D&C may be advised for bleeding control or to detect and remove retained (unpassed) pregnancy or placental tissue after a miscarriage, abortion, or birth.
Prolonged or excessive vaginal bleeding – In certain situations of prolonged or severe uterine bleeding that does not respond to medical therapy, a D&C may be performed.
PROCEDURE FOR D&C
A D&C may be done in a hospital operating room, an outpatient clinic, or an outpatient surgery center. During the process, your blood pressure, pulse, and blood oxygen levels are all measured. The operation itself usually takes between 15 and 30 minutes to complete.
General, regional, or local block anesthesia might be used during the surgery. The kind of anesthetic used is determined by the purpose of the surgery as well as your medical history.
AFTER D&C CARE
Following the procedure, you will be resting in a recovery or post-anesthesia care area for some time. This permits you to recuperate from whatever anesthetic you may have had while also monitoring for excessive vaginal bleeding or other issues. The length of time you spend in the recovery room is usually determined by the kind of anesthetic you had and may vary from 30 minutes to a few hours. You may have nausea and vomiting if you were given general anesthesia, which may be managed with drugs.
Home recovery – You should be able to resume most of your normal activities within a day or two. Mild cramping and spotting may continue for many hours or days; cramping may be managed with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). You should not insert anything into your vagina (tampons, douches) at this period and should inquire about when you may safely engage in sexual intercourse. If you have not yet reached menopause, your next menstrual cycle should arrive between two to six weeks following the operation, depending on the cause for the D&C.
dilation and curettage uterus cervix health
No Comments