
: Admin : 2022-06-30
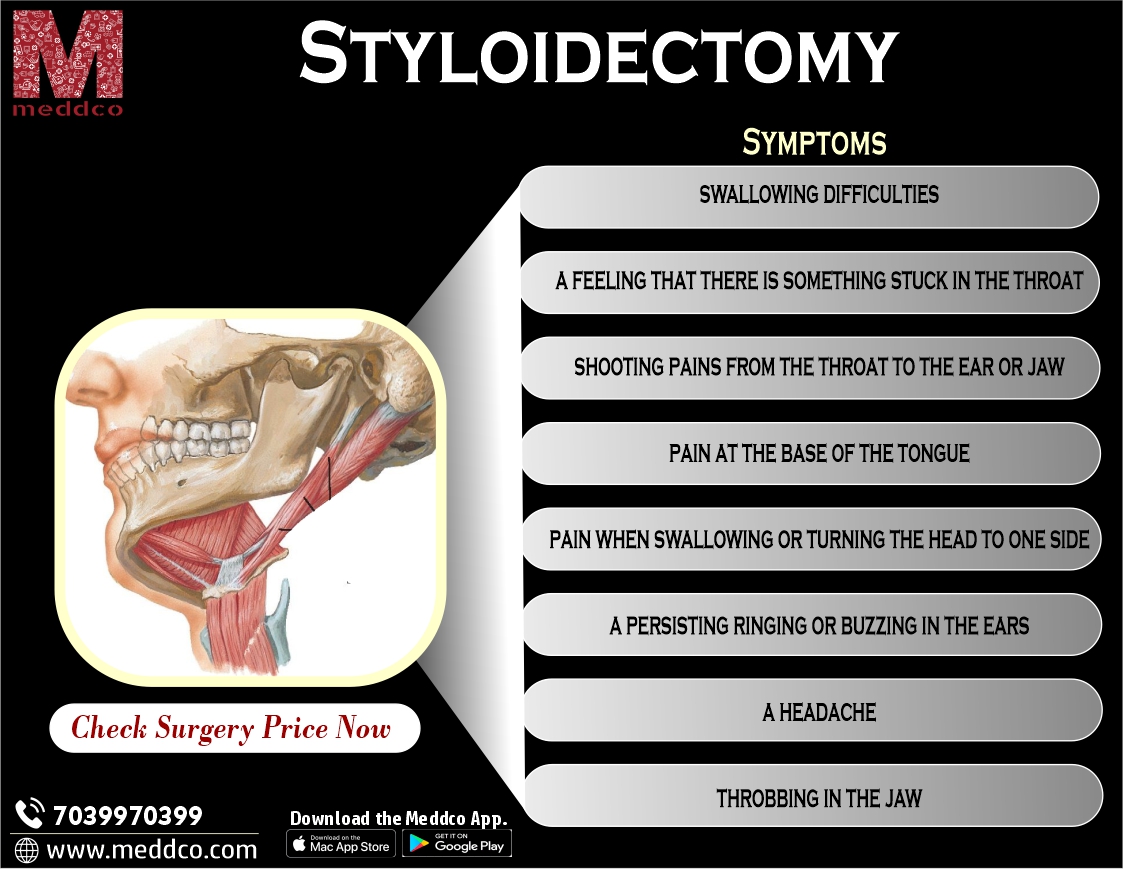
Eagle syndrome is an elongated styloid with related signs and symptoms of recurrent facial or throat pain. In this article, we present Eagle syndromeands uncommon trigeminal nerve involvement. Notably, patients developed classic post-styloidectomy trigeminal neuralgia. Eagle syndrome is a complicated condition resulting from an elongated styloid mode related to a gigantic form of symptoms. Although the maximum normally associated with throat and neck pain is worsened by head rotation, swallowing, or chewing, it can also be related to pain in a V3 trigeminal distribution. Although the glossopharyngeal nerve is normally implicated in Eagle's syndrome, involvement of the mandibular nerve is possible. Eagle syndrome, a probable etiology of a stupid pain along the jaw line or temple, should be considered. Pain on this distribution is an unusual but viable symptom of Eagle syndrome that is effortlessly under pressure with various patterns of facial discomfort, including temporomandibular joint disease or dental pain.
●Prognostic elaboration
If a patient's previous medical records were non-contributory and there were no extraoral findings, then all possible alternative causes of pain, odontogenic diseases, oral, dental, neuralgic and muscular and temporomandibular injuries had been eliminated.
The differential prognosis was mainly based on understanding situations that mimicked the form of pain, which had been neatly ruled out to arrive at a conclusive prognosis. The differential prognosis includes, but is not limited to, glossopharyngeal neuralgia, superior laryngeal neuralgia, occipital neuralgia, sphenopalatine neuralgia, intermediate nerve neuralgia, headache migraine, cervicogenic headache, oromandibular problems temporomandibular joint problems, including, third molar or distorted, defective dental prostheses, Sialolithiasis, Tonsillitis, Otitis Mastoiditis, Foreign bodies, Inflammatory and neoplastic tactics with within the oropharyngeal and esophageal areas and various psychosomatic diseases.
Intraoral palpation of the pharyngeal area is performed using the index finger under local anaesthesia and using 15% lidocaine spray in the pharynx. Palpation of the pharyngeal area revealed a point of bony growth, which was felt underneath near the smooth tissues of the pharynx. Tenderness on palpation in each of the cases uncovered elongated styloid tactics, which were absent on the contralateral facet and consequently, the prognosis of elongated styloid manners was made.
●Surgery-
●Anatomy-
The styloid mode is a thin, elongated cylindrical bony projection that lies anteromedially to the mastoid mode. Its period varies from 2 to 3 cm. Behind the styloid is the facial nerve, which emerges from the stylomastoid foramen. Medial to the styloid, moving posteriorly to the anterior, is the internal jugular vein and the internal carotid artery. Medial to the top of the styloid is the advanced constrictor muscle and the pharyngobasilar fascia, which lie adjacent to the tonsillar fossa. The external carotid artery is lateral to the top of the manner, which
forks into the superficial temporal and maxillary arteries. The stylohyoid ligament extends from the styloid to the maize minor of the hyoid bone.
●Technique-
After being identified as cases of Eagle syndrome secondary to the elongated styloid process, patients underwent surgical removal of the elongated styloid bone via an intramural approach.
●Anesthesia-
Local anaesthesia is administered as submucosal infiltration along with the medical problem of the ascending Remus and the locus of the styloid manner after administering the intraoral mandibular nerve block in use.
●Results-
The surgery was uneventful, and follow-ups found that sufferers remained symptom-free after the surgery.
●Conclusion-
Eagle syndrome is an unprecedented disease responsible for polymorphic signs and symptoms of the head and neck, which occur regularly with a poor prognosis. The prognosis of Eagle's syndrome is based on the presence of suggestive clinical symptoms and pain-related symptoms on palpation of the styloid mode in the tonsillar fossa; tremendous lidocaine observes a lengthening of the styloid mode on 3D CT. The maximum curative remedy normally proposed is styloidectomy, which allows the entire decision of signs and symptoms in most cases. This way can be achieved through a transoral method or a transcervical method. After reviewing the embryology and anatomy of the styloid diaphragm region, the authors describe the transcervical styloidectomy approach conducted by their department. This easy approach is based on anatomical imperatives designed to limit working hours and keep away from damage to neurovascular structures.
eagle syndrome facial pain throat pain styloid
Related Articles
No Data Found
No Comments