
: Admin : 2021-12-27
What are the diagnostic procedures to know the cause of the disease?
Life on earth has evolved into a complex network of integrated organ systems that have adapted themselves to physical, environmental and socio-economic changes in the world. With the invention of scientific research-based devices, information technology, computers to advanced palm-sized widgets, the world has solutions to every complication and problem. Natural calamities, pandemics from mutations of micro-organisms and diseases from damage or death of tissue, continue to harm people globally, but man has made continuous, ceaseless efforts to survive through all odds and challenges of nature that harm lives.
The science of medicine has an answer, remedial solutions to every disease. Medical science has been categorized into different branches according to different organ systems. Scientists and medical professionals have developed diagnostic procedures that are technologically sound, to decipher any diseased condition. These advanced techniques have made it convenient, painless and swift to diagnose every pathology in human beings. Doctors in present times do not rely on general examination or history nor on objective symptoms but mainly on diagnostic tests. Diseases found in human beings in the past few decades have affected vital organs of the body causing detrimental harm and death to people all over the world. Most of the diseases do not show a pattern of symptoms that can be tracked by basic physical examination or taking a medical history of the patient. The mutations, variants, of different types of micro-organisms and several new species have caused many complex diseases. Diseases have been grouped according to each system in the books of medicine. The classification range from upper respiratory tract infections, digestive disorders, diseases of the nervous system to carcinomas that destroy the lives of patients. A detailed study and careful observation by skilled medical professionals have made it possible to distinguish different clinical conditions. The differential diagnosis is made more precise and authentic through diagnostic tests and laboratory investigations through advanced technology. The fundamental, deep-rooted cause of every disease can be investigated, navigated in every manner or facet to conclude the final treatment protocol. Microorganisms infecting organ systems can be examined under laboratory findings, microscopic observations help to identify the variant that has caused the disease. Similarly, scientific research and inventions on technology-driven diagnostic aids locate the area and extent of the spread of diseased conditions.
The common diagnostic procedures conducted for sound clinical understanding and differential diagnosis of different pathological states are as follows.
X rays are electromagnetic waves done as an imaging procedure that magnifies images of parts of the body. The diseased parts can be studied on the X-ray plate through a spectrum of electromagnetic waves. It is the most common method to locate stones, upper respiratory tract infections and diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
CT scan or computerised tomography is a combination of a series of X-ray images taken from different angles of the body with cross-sectional images of bones, blood vessels and soft tissues inside a patients body. It is done as a detailed study to understand pathology as it gives more information than a plain X-ray.
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) is done using magnets and radio waves to scan organs and internal body parts. It is used to diagnose ligament tears to tumours.
ULTRASOUND is an imaging technique that creates images of tendons, muscles and internal organs thereby finding the source of the disease or cause of the pathology.
What is intravascular ultrasound?
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. Coronary arteries pump blood to the heart. These arteries become narrow when atheromatous plaques build within the walls of the coronary artery. An increase in cholesterol with a high rise in triglycerides, LDL, HDL from unhealthy junk fatty foods, can cause the formation of atherosclerotic lesions in the lumen of coronary arteries. It develops stenosis of the arteries causing a decrease in blood flow to heart muscles. If the condition is not treated, the patient may collapse from congestive cardiac failure.
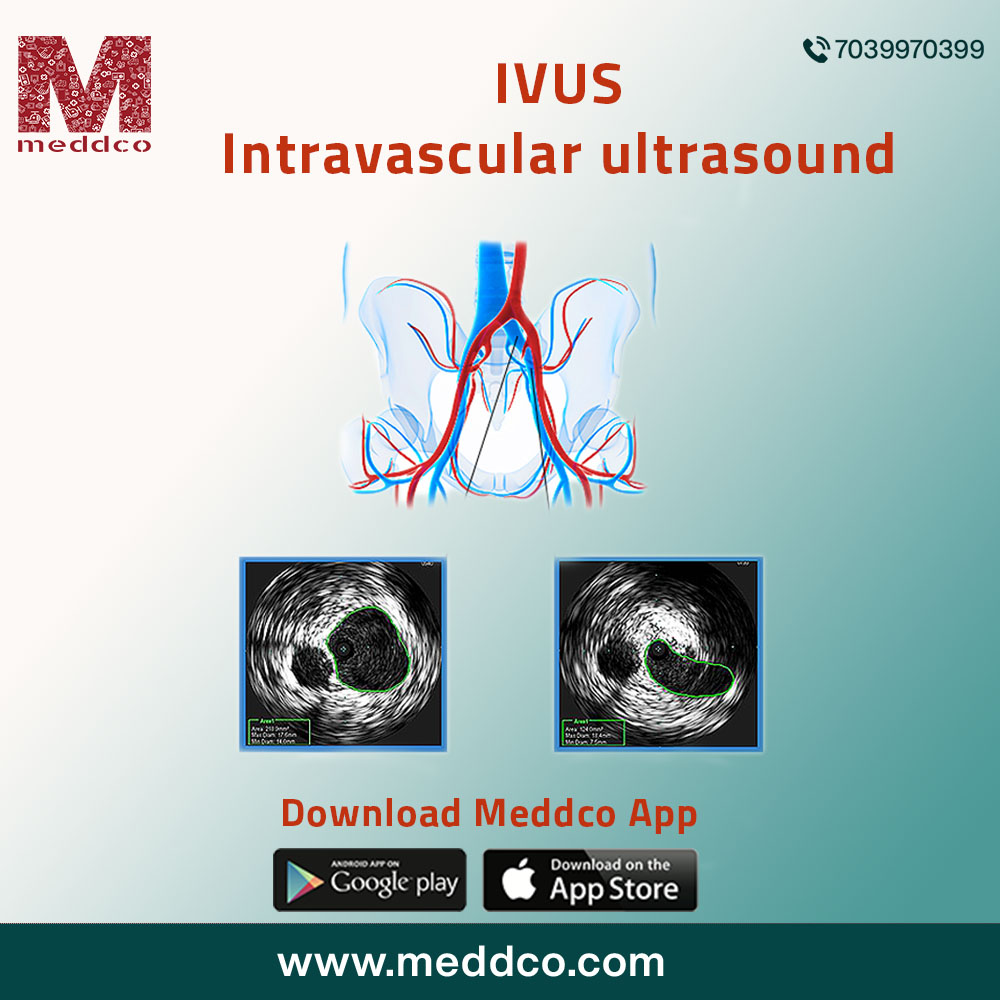
Several preliminary diagnostic tests and procedures are done to locate the atherosclerotic changes in the walls of the coronary artery. Intravascular ultrasound is one such important diagnostic procedure. IVUS is a medical imaging methodology where a specially designed catheter is used with a miniature ultrasound probe attached to the distal end of the catheter. The proximal end of the catheter is attached to a computerised ultrasound device. The advanced application of ultrasound technology such as piezoelectric transducer aids the doctor to visualize the inside of blood vessels. The ultrasound procedure determines, scans the progressive damage to the lumen of coronary arteries from atheromatous plaques. The amount and volume of blood supply to coronary arteries can be evaluated, analyzed when the stenosis in the walls of the coronary artery decreases the blood flow to the heart.
Angiography is a specific diagnostic procedure to understand diseases of the heart, but Intravascular ultrasound is useful in situations where angiographic images fail to scan or visualize lumen segments adequately. The multiple overlapping arterial segment lesions can be assessed and seen on the intravascular ultrasound scan. IVUS is an evolved technique, believed to be a useful research-based diagnostic method for modern invasive cardiology. It is predominately used in the research process to understand the behaviour of atherosclerotic plaques in human beings.
What are the advantages of using intravascular ultrasound?
IVUS is an authentic accurate procedure that enables a doctor to distinctly visualize the lumen of the artery for atheromatous plaques laden with cholesterol loaded white blood cells. Research studies were conducted using the IVUS method to know how coronary artery lesions cause myocardial infarction.
The research report has revealed a thorough understanding and a diverse perspective of the extent of the spread of atheromas in walls of coronary arteries. These studies have prevented the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Doctors study these images to understand how severe coronary artery stenosis is, thereby focusing on the prevention of heart attack in vulnerable patients.
The current day clinical advantage of IVUS is to treat the complex lesions to determine how well an intracoronary artery stent can be implanted in a damaged wall that has caused the stenosis within coronary arteries. It is done to decide the method or treatment procedure whether angioplasty or bypass surgery.
How is IVUS done?
A patient is prepared for the procedure by asking him to stay on a certain diet or nil by mouth during the day the surgery is scheduled.
A patient is advised to stop taking blood thinners on the day of the procedure. A nurse will start an intravenous drip to administer medicines during the procedure. The patient lies in the supine position while the nurse places electrodes on the chest. The electrodes are attached to an electrocardiograph monitor. The patient is given mild sedative just before the procedure. A doctor uses a local anaesthetic to numb the groin area. A short hollow tube is inserted into the groin. A catheter is then inserted through this tube that is threaded to the arteries of the heart. Through this catheter, a wire with an ultrasound tip is passed into the coronary arteries. The ultrasound device provides a series of cross-sectional images of coronary arteries. These scans guide the doctor to visualize the pathology by identifying the spread and diameter of the atheromatous plaques. IVUS procedure takes about 60 minutes time and is the most important diagnostic test to decipher diseases of the heart.
After the procedure, the patient is allowed to rest with pressure applied to the groin to prevent bleeding. A dressing is done near the area of the groin at the site where the catheter was inserted. The patient needs to stay overnight for observation in the hospital after the procedure. Later the pressure dressing is removed. A doctor then decides the further treatment procedure for the patient, after studying the reports of IVUS if the patient requires an angioplasty or a bypass surgery.
What are the interpretations after IVUS is done?
IVUS is a standard procedure to measure, evaluate and visualize coronary artery damage. The information about the lumen of the coronary artery and its anatomy, tissue characteristics of the atheromatous plaques formed in the coronary artery. It is a guide to deciding on endovascular implants. IVUS images feature three-dimensional images of the arterial wall and its lumen. Online measurements of plaques can be determined of each atheromatous plaque from every cross-sectional image. Fibrous and calcific changes from plaque formation can be spotted, measured in the lumen of coronary arteries. It differentiates between stable and unstable plaques. Stable plaques have more calcified fibrous tissue. Unstable plaques have a large necrotic core covered by a fibrous cap that appears to form a thrombus.
Peripheral artery disease develops when plaques develop in the walls of arteries of legs that reduce blood flow. Advanced stages of peripheral artery disease are associated with a high risk of cardiovascular diseases, amputation and mortality. IVUS study of these peripheral arteries is a guide to doctors as an imaging technique to diagnose the occlusion caused by plaques.
What are the recent advances in IVUS technology?
IVUS uses miniature ultrasound transducer that is mounted in tge tip of the catheter inserted within the groin to direct the damage done to coronary arteries by atheromatous plaques. This advanced technique captures images of the lumen, plaques and stenosis of the vessel walls. The vessel morphology due to the plaques determine the size and measure the actual diameter of the lesion for the size of the stent and how to position the stent within the lumen of the coronary artery. A co- registered view from angiography and fractional flow reserve and instant wave free ratio from different images of IVUS help to understand the severity and location of lesions. These advanced method identifies the main arterial lesion that requires an intensive urgent treatment procedure by grafting a stent.
Near infrared spectroscopy IVUS helps to detect the plaques with high lipid content, those that are most likely to cause a myocardial infarction. These vulnerable plaques once identified, by analysis of their composition, reduce the risk of mortality through an emergency angioplasty or a bypass surgery to save lives of patients.
How does IVUS improve the clinical conditions of patients suffering from coronary artery disease?
Patients who are advised to undergo IVUS procedure have shown clinically sound good results post stent implantation. As compared to angiography, IVUS guided procedures were longer in duration, aimed to use stents of greater diameters and lengths. It has revolutionized the approach in treating coronary artery disease, has improved the clinical conditions of the patient with an increase in life expectancy post surgery. IVUS study also helps to locate iliofemoral venous obstruction.
In cases of peripheral artery disease, it has shown improved outcomes with reduced rates of mortality. The dissections obtained through angiography are often overlooked, under diagnosed, are not detected and left untreated. The dissections obtained through IVUS demonstrate the severity of lesions that remain undiagnosed from other methods of investigation. IVUS study gives several cross sectional images of one diseased arterial segment in comparison to angiography, so it is predominately a preferred procedure by interventional radiologists and cardiologists worldwide.
intravascular ultrasound ivus
No Comments