
: Admin : 2021-12-02
Obesity is a complex disease where the body mass index is above 30, causing an increase in amount with an irregular distribution of fats. The abnormal distribution of body fats invites several diseases in the body. Obesity is high a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. With an alarming rise in obesity in different parts of the world, a surgical medical intervention to reduce or cut down body fats is advised by health care professionals all across the world. Surgery done for weight reduction is termed bariatric surgery or metabolic surgery. Patients with a body mass index of 40 and between the age group of 16 to 70 years, can undergo bariatric surgery. A brief medical history is noted by the surgeon observing vital signs prior to the surgery being scheduled by the doctor.
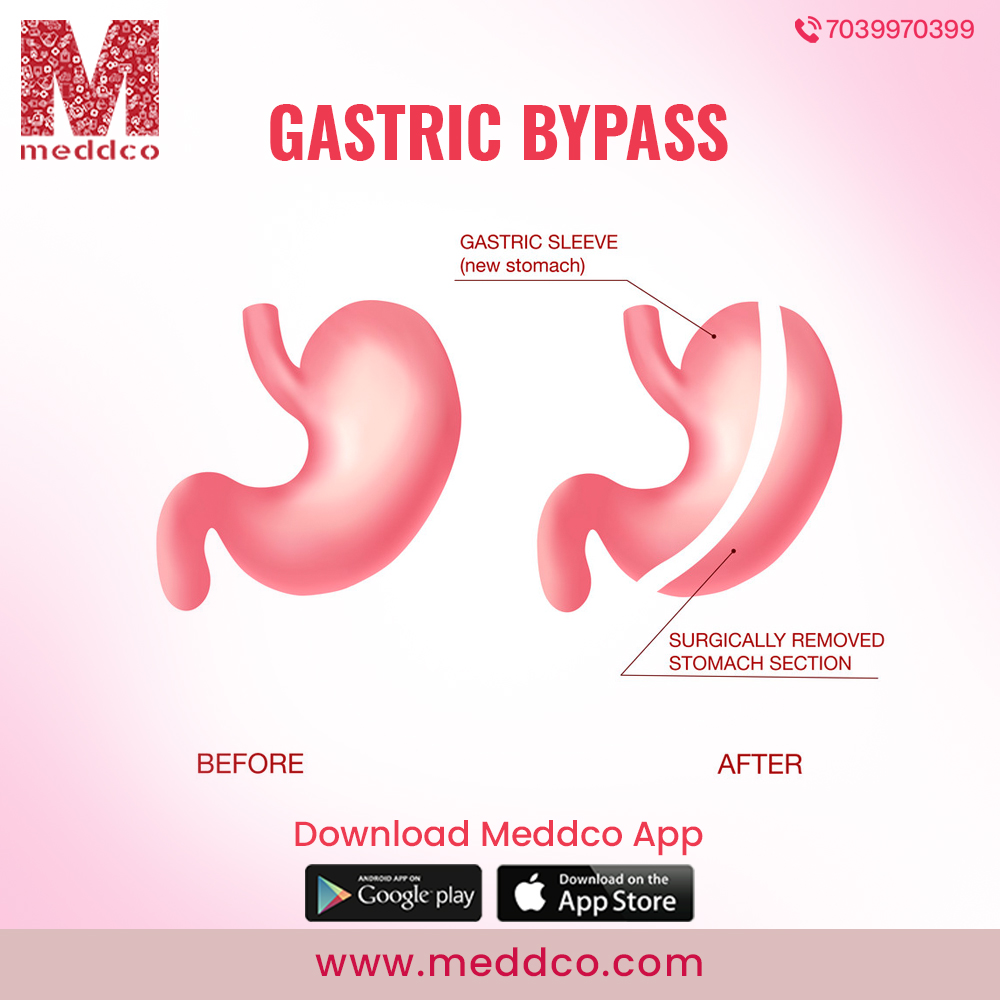
WHAT IS GASTRIC BYPASS SURGERY?
Gastric bypass surgery is a weight loss surgery, an advanced technique to divide the stomach into an upper and lower chamber through an anastomosis connecting the small intestine. Surgeons have invented several methods to form a bypass from the stomach connecting the intestines which lead to a considerable reduction in the volume of body fats. The physiological functions are altered followed by physical digestion of food that does not cause accumulation of excess fats.
Gastric bypass surgery is advised for patients suffering from obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, sleep apnoea and many more comorbidities.
WHAT METHODS ARE DONE?
Laparoscopic surgery is one form of an invasive procedure where a telescope is used to view incisions made through aid of specialised devices. The surgery can be done skillfully by viewing areas that can be connected through a bypass between the stomach and intestines.
Mini gastric bypass surgery is another method that creates a long tube along the lesser curvature of the stomach. A loop of the small intestine is then connected to this tube at about 180 cm from where the intestines start.
The endoscopic duodenal jejunal bypass connects a bypass between the duodenum and mid-jejunum. This method causes malabsorption of fats, starch and various fat-soluble vitamins. The unabsorbed fats directly pass into the large intestine where the final process of digestion takes place. This affects nutritional assimilation with an increase in weight loss.
gastric surery weightloss weight obesity bodyfat
No Comments