
: Admin : 2021-08-30
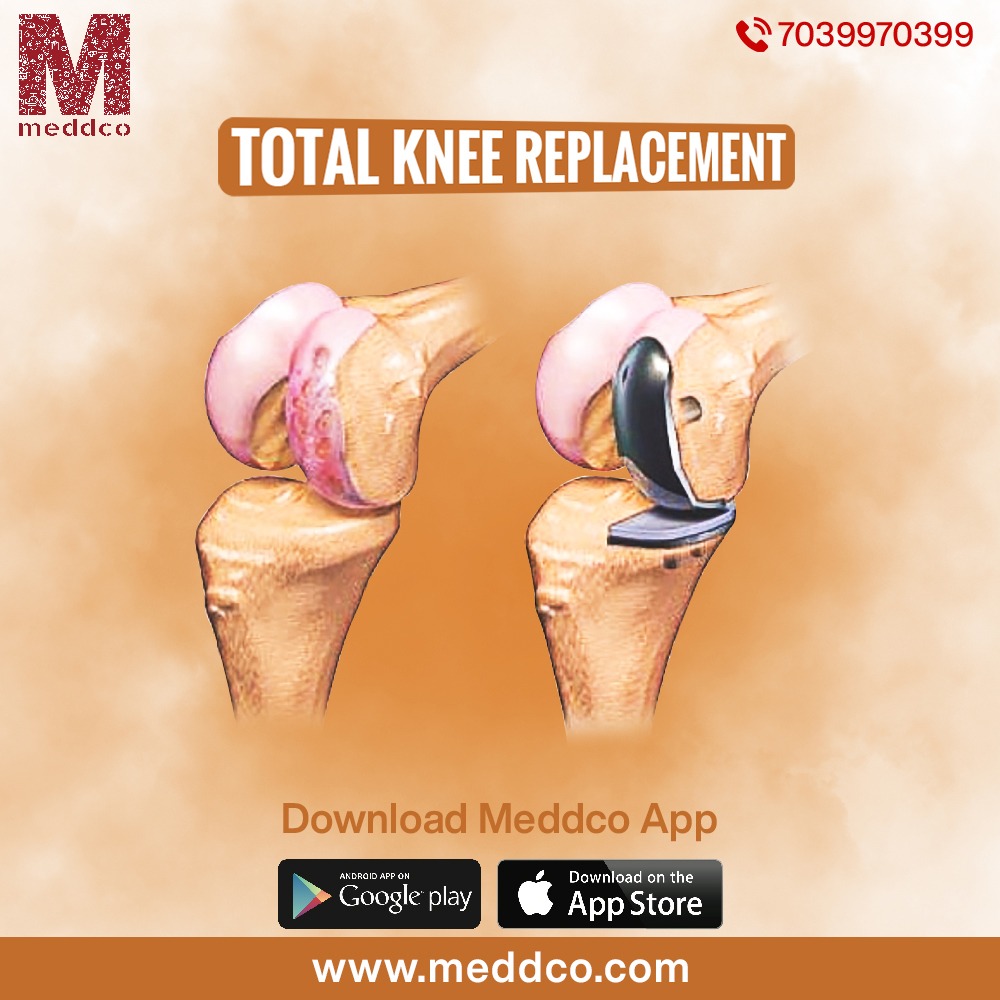
Knee replacement, commonly known as knee arthroplasty or complete knee replacement, is a surgical operation used to resurface an arthritis-damaged knee. Metal and plastic components, as well as the kneecap, are utilised to cap the ends of the bones that make up the knee joint. Someone with severe arthritis or a severe knee injury may benefit from this procedure.
The knee joint can be affected by several types of arthritis. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that primarily affects middle-aged and older persons. It can result in the destruction of joint cartilage and neighbouring bone in the knees. Rheumatoid arthritis, which causes synovial membrane inflammation and excess synovial fluid, can cause discomfort and stiffness. Traumatic arthritis, or arthritis caused by an injury, can harm the cartilage in the knee.
The purpose of knee replacement surgery is to resurface damaged areas of the knee joint and reduce knee discomfort that cannot be controlled with conventional treatments.
What is the cost of total knee replacement surgery?
| City | Price |
| Mumbai | 155158 |
| Delhi | 170076 |
| Hyderabad | 130000 |
| Kolkata | N/A |
| Lucknow | 190000 |
| Chennai | N/A |
| Jaipur | 97500 |
| Pune | 261700 |
| Patna | 149066 |
| Bengaluru | N/A |
Reasons for the procedure
Knee replacement surgery is a treatment for knee pain and disability. Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent ailment that necessitates knee replacement surgery.
The deterioration of joint cartilage is the hallmark of osteoarthritis. Damage to the cartilage and bones restricts movement and may result in pain. Because of the pain, people with severe degenerative joint disease may be unable to perform regular tasks that require bending at the knee, such as walking or climbing stairs. Because the joint is unstable, the knee may enlarge or "give way."
Other types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis and arthritis caused by a knee injury, can also cause knee joint deterioration. Furthermore, fractures, damaged cartilage, and/or torn ligaments might result in irreparable knee joint injury.
If medicinal treatments are ineffective, knee replacement surgery may be an option. Among the medical therapies for degenerative joint disease are, but are not limited to, the following:
Your doctor may also propose knee replacement surgery for other reasons.
Prior to the procedure
During the procedure
After the procedure
In the hospital
You will be brought to the recovery room for observation following the surgery. You will be transported to your hospital room once your blood pressure, pulse, and respiration are steady and you are aware. Knee replacement surgery normally necessitates a few days in the hospital.
Following surgery, it is critical to begin moving the new joint. Soon after your total knee replacement surgery, a physical therapist will meet with you to create an activity regimen for you. To begin physical treatment, a continuous passive motion (CPM) machine may be employed. While you sleep, this gadget moves your new knee joint through its range of motion. Medication will be used to control your pain so that you may engage in the workout. You will be given an exercise regimen to follow both whiles in the hospital and after you are discharged.
You will be sent home or to a rehabilitation facility. In either scenario, your doctor will make arrangements for you to continue receiving physical therapy until you rebuild muscular strength and range of motion.
In-home
Once you've returned home, it's critical to keep the surgery area clean and dry. Bathing instructions will be provided by your doctor. During a subsequent appointment visit, the stitches or surgical staples will be removed.
You may be urged to elevate your leg or apply ice to the knee to assist in minimise swelling.
As directed by your doctor, use pain medication for soreness. Aspirin and other pain relievers may raise the risk of bleeding. Take only drugs that have been prescribed to you.
knee replacement surgery Rheumatoid arthritis Meddco total knee replacement surgery
Related Articles
No Comments