
: Admin : 2022-01-28
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The nervous system originates from the brain extends lower down to back, to form the spinal cord, coordinating, functioning, to conduct physiological activities in different organ systems through a network of nerve cells. Brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system. The complex network of nerves that conduct nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to all other parts of the body form the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system connects the central nervous system to limbs, organs and skin. The function of every organ depends on stimulus received from different parts to a definite response from the brain to every specific action within the body. Organs unite to form organ systems that work in a collective organised manner for the human body to work in harmony. Nerves receive these impulses, convey this sensory information through the spinal cord to the brain. Motor impulses generated in the brain in response to sensory information, reach organs and limbs through peripheral nerves to develop, perceive, distinguish and decipher every stimulus. The response from the brain and spinal cord that reaches organs of the body through a set of peripheral nervous systems helps every system of the body to work consistently in coordination in a balanced rhythmic manner. The peripheral nervous system is a matrix or maze of nerves that receive information and conduct impulses from the brain in response to every external stimulus. The peripheral nervous system transmits a stream of information in the form of nerve impulses to and from the central nervous system thereby connecting every organ to the brain.
The peripheral nervous system is divided into somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. Voluntary actions such as walking are controlled by somatic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for vital functions of body such as heart beat, breathing and digestion. The somatic nervous system carries sensory data from external stimuli received from either of these special senses—hearing, sight, touch to the brain, that later generate messages to initiate and control voluntary activities.
The somatic nervous system is made up of afferent or sensory neurons that carry information from external stimuli from outside sources or internal organs – muscles, glands and skin. The message reaches the brain through sensory neurons. Motor neurons from the efferent channel conduct impulses from the central nervous system to different parts of the body in response to external and internal stimuli. A neural pathway composed of a synchronous immediate reaction to every action or stimulus that connects the central nervous system with every body part makes the peripheral nervous system. A person instantaneously responds to external expressions like heat or loud noise through motor impulses generated from the brain which travels through efferent neurons to save himself from harmful irritants. These are voluntary actions, of which a person is aware, to take prompt decisions before it causes any damage.
Several involuntary actions take place within human body. A person is unaware of his heart beat, pulse rate, digestion and pattern of breathing. These involuntary functions are controlled by autonomic nervous system—which is a part of peripheral nervous system. These actions are governed by autonomic nervous system without a person being conscious of the rhythm of each of these involuntary functions.
Autonomic nervous system is further divided into sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. A sympathetic response is towards any situation in a person’s life when it is threatening or frightful. He feels increase in heart rate, profuse sweat with pupils dilated with an action to free himself from a dreadful, fearful experience. The para sympathetic nervous system on the contrary relaxes a person, reduce heart rate, sweating, tries to control rush of blood flow, by allowing body to rest, ease from any situation that creates panic.
There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves that from peripheral nervous system, extend from spinal cord, reach out to muscles and glands carrying sensory and motor signals from brain. About 12 pairs of cranial nerves are attached to the brain. The function of these nerves is to transmit sensory information from ears, eyes, nose and mouth and conduct motor response from brain to these organs that carry special senses. These are different components of peripheral nervous system which work unitedly to maintain body’s dynamic homeostasis.
What is peripheral nerve tumour?
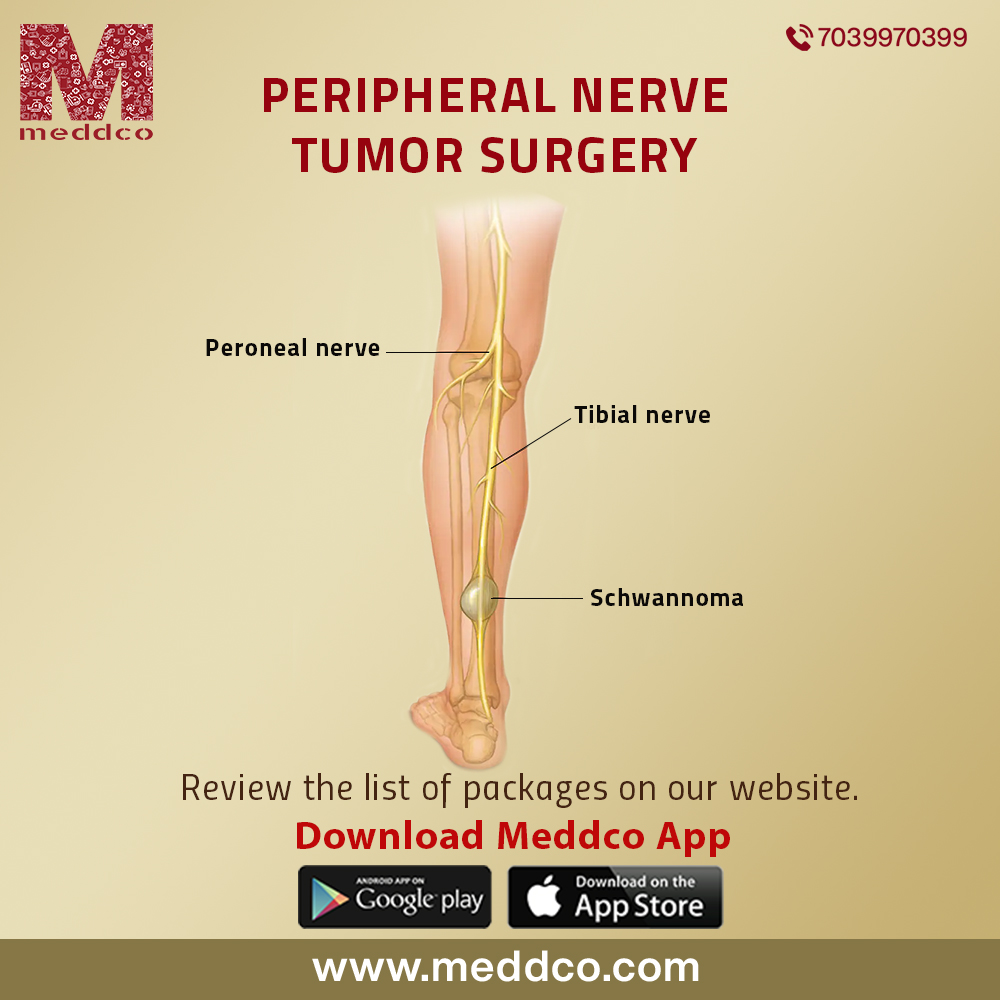
Peripheral nervous system radiates throughout the body through complex network of nerve fibers. Unlike brain and spinal cord that constitute the central nervous system, being well protected in body structures skull and vertebral column respectively, peripheral nervous system does not have any bony supportive sheath that envelope around a diverse labyrinth of nerves. It broadly spreads in all parts of the body, is under maximum risk to different diseases, infections and injuries. Peripheral nerve disorders cause damage to normal functions of nerve fibers causing their distortion of transmission of messages between brain and different parts of the body. Metabolic disorders like Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and endocrine diseases cause peripheral nervous system. Viral infection cause disease of peripheral nervous system called Gullain Barry Syndrome. Compression of nerves in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis or chronic kidney disease can damage peripheral nervous system. Cancerous growths or tumours cause pressure on peripheral nerves which damage its normal functions. A peripheral nerve tumour is a benign or malignant growth within the nerve or sheath surrounding it. These tumours are rare, benign in nature and at times malignant. Neurofibroma, neuroma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour, peripheral nerve tumour, perineurioma and schwannoma are common types of tumours found in peripheral nervous system. The incidence of these tumours is upto 5% with symptoms that cause severe deterioration of nerve function.
Diagnosis of peripheral nerve tumours is through ultrasound, CT scan, electromyogram, nerve conduction study, MRI, tumour and nerve biopsy.
What are symptoms from peripheral nerve tumour?
Tumours in peripheral nerves cause –
Swelling or lump, a growth under the skin. Pain, tingling and numbness are also felt by the patient. The lump causes weakness with loss of sensation in the affected part. Dizziness with loss of balance is an associated symptoms observed in patients suffering from peripheral nerve tumour. The function surrounding the nerve or an organ is affected by the tumours which gradually gets retarded. In complicated advanced cases, symptoms may worsen causing permanent impairment or distortion of organ function. A mass or lump of soft tissues can be felt with symptoms of fever and weight loss.
Peripheral nerve tumours are found in patients having neurofibromatosis. Few other tumours are caused from an inherited dysfunctional gene or damage to nerves from an injury or surgery.
An early medical intervention becomes crucial for treating peripheral nerve tumours. Surgery is often the choice of treatment apart from chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
What is peripheral nerve tumour surgery?
When the tumour in the peripheral nerve gets enlarged to produce agonising symptoms a surgery is the only remedial solution or medical approach that saves life of patient. Aim of this surgery is to remove the entire growth or lump of cancerous tissue without damaging healthy nerves and tissues. Technology has made possible to locate and determine the size of remote tumours. High powered microscopes, advanced technology driven computerised surgical devices have made it easier to distinguish a healthy tissue from the abnormal mass or cancerous lesions. These techniques help the neurosurgeon to remove the tumours thereby preserving the healthy tissues and organs of the body.
STEREOTACTIC RADIOSURGERY – This surgery is done to treat peripheral tumours in or around the brain. A Gamma knife radiosurgery is done by administering radiation on the tumour without making any incisions.
The tumor surgery can be done using powerful microscopes. General anaesthesia is administered to the patient. Electromyogram with use of concentric needles inserted into the muscles is done to record the surgical procedure. The peripheral nerves that shows development of a tumour is stimulated. A small incision is made through the skin, near the tumour, later the tumour is excised taking care to prevent damage to surrounding healthy tissues. If the tumour is present within the nerve sheath, abnormal mass is excised keeping the nerves undamaged.
Radiotherapy, post surgery kill the cancerous cells that could not be excised through surgery. Chemotherapy is used to shrink the tumour to prevent further growth or slow a progressive increase of cancerous lesions. Recovery post surgery takes 6 to 12 weeks.
Patient should be aware about the risk of recurrence of tumours post surgery. He should approach a medical professional at regular intervals for screening, monitoring any abnormal growth through specific diagnostic tests. Most of the peripheral nerve tumours are benign which may recur. So, follow up visits to a neurosurgeon help in early management of an abnormal growth. Malignant growths are rare, but it once the lesions deteriorate surrounding healthy tissues, physiological functions of these tissues are impaired causing life threatening damage to distant vital organs. A patient who has undergone a peripheral nerve tumour surgery requires certain life style management. A thorough detailed analysis of any minor symptoms from a pannel of expertise such as radiologist, neurophysician, neuro surgeon and psychologist who guides the patient to observe every deranged state that can be treated should be fundamentally educated to every patient. A healthy, systematic, timely medical approach in peripheral nerve diseases can increase life expectancy in patients.
peripheral tumour surgery
No Comments