
: Admin : 2022-01-14
What are birth defects?
The process of giving birth to young ones to continue life on earth is termed as reproduction. A child inherits characteristics or genetic traits from his parent. In complex organisms, sexual reproduction takes place where by union of sperm and egg cell a zygote is formed. The zygote contains 46 chromosomes—genetic properties getting 23 from male sperm cell and rest 23 from female egg cell. The fertilized zygote develops gradually within the uterus into foetus. Zygote divides through the process called mitosis. Mitosis is a form of cell division in which each cell doubles – one cell becomes two, two cells unite to form four to develop into organ and organ systems. As zygote matures into foetus, several factors influence the process of growth, multiplication of cells into organ and organ systems. A foetus who inherits characteristics from sperm cell and egg cell may be born with chromosomal abnormalities, genetic predisposition to certain diseases and birth defects.
A new born baby having a visible physical abnormality, internal chemical abnormality or imbalance in any part of the body caused by genetics, infection, radiation, drug exposure or there may be an unknown iteology for birth defect to form and develop in a child. The first three months or the first trimester of pregnancy is the most important phase when organs of baby get their shape, structure from which an organ system is formed. Most birth defects are formed during the first trimester of pregnancy. Some birth defects are formed in the last trimester of pregnancy. A handicap may occur from incorrect union or fusion of cells during mitosis or cell multiplication process forming an abnormal mass of cells, diseased predisposition or chemical imbalance that appear as birth defect in a new born child. A child and his parents sense the discomfort while performing daily routine activities. When it is visible as a physical abnormality, it can be treated by a skilled medical professional. If it manifests as a chemical imbalance, genetic trait or a predisposition or internal disorder, diagnostic tests help to identify the defect which can be rectified by treatment if within the scope of conventional medical science. Most of these birth defects can be identified during the early phase of development or first trimester of pregnancy. Medication , timely medical intervention can save the child from irreversible damage caused by certain birth defects.
What is cleft palate?
A normal healthy growth of foetus during nine months or full term pregnancy inside the womb of mother is of paramount importance. There are different factors that influence the growth of foetus in the uterus. Genetic, environmental factors, diet of mother, gestational diabetes in mother, and what medication she takes during pregnancy play a vital role in growth of foetus. As the development of zygote into an embryo occurs, by growth and multiplication of cells, under the control and power of different natural and artificial forces, in terms of environment, food, genes and medicines, a healthy normal birth of a baby as planned by team of doctors results after a full term pregnancy.
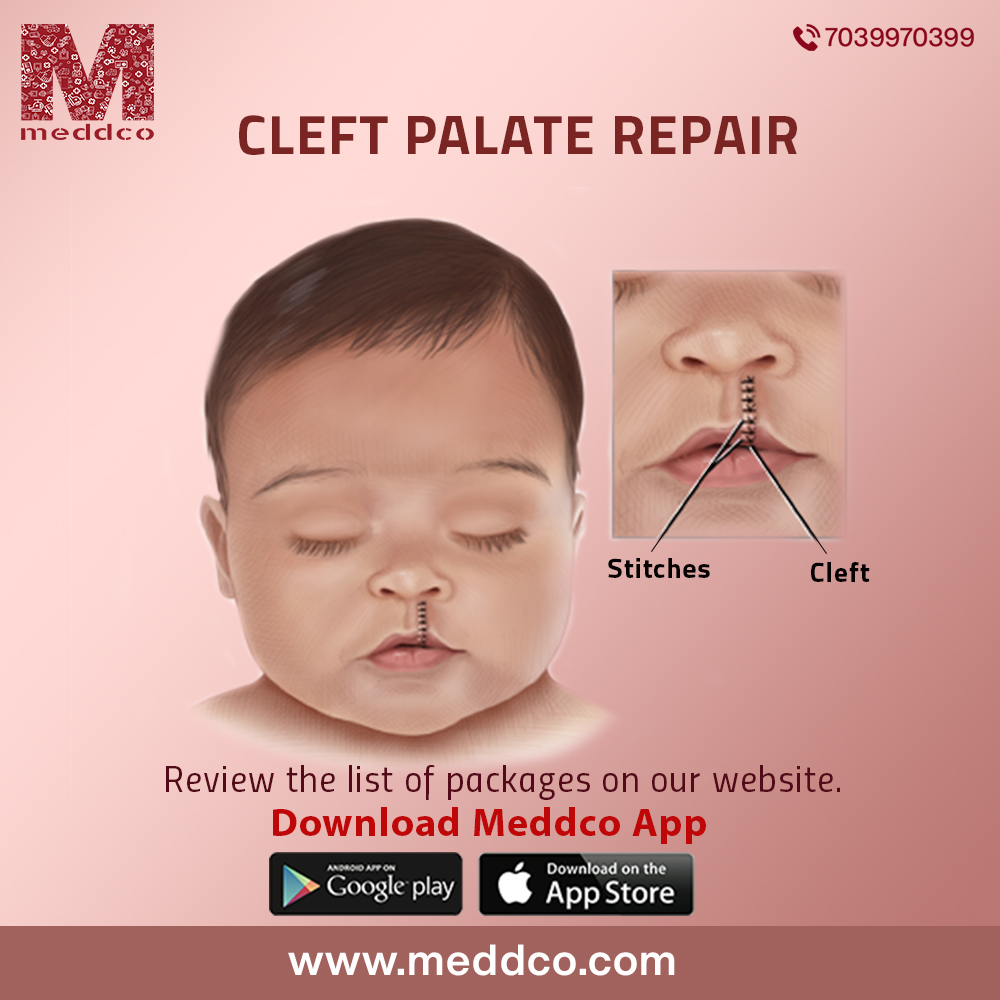
During cell multiplication, mitosis, growth of cells that mature into a foetus gradually during every trimester when a woman is pregnant, is a physiological process of reproduction or giving birth to a healthy baby. However, if fusion of cells is atypical, unusual and malformed during development of an organ, an abnormal physical defect may be seen in the child. The roof of mouth or palate is formed between sixth and ninth weeks of pregnancy. The hard palate in the bony plate in the front of roof of mouth directly behind upper teeth helps food to move back through the mouth. The soft palate is at the back of the mouth, made up of soft muscles which closes against the back wall of the throat during swallowing bolus of food. The soft palate also contributes during speech mechanism and lets the air out depending upon the type of sound. A cleft palate happens if the tissue that makes up the roof of the mouth does not join completely together during pregnancy. An incomplete fusion of tissues during palate development resulting in opening in upper lip, palate or both when the baby is born is termed as cleft palate. Some babies are born with both front and back parts of the palate open depicting a strange facial contour from non fusion of tissues palate within buccal cavity. An abnormal visible gap near the opening of roof of mouth is observed in a child born with cleft palate.
A cleft palate is the most common congenital deformity or birth defect. On an average about 1 in every 500-750 births result in cleft palate through out the world. An epidemiological survey proves that every three minutes somewhere in the world a baby with a cleft palate is born. It is common in Asian countries especially India due to folic acid deficiency in females. Its deficiency causes increased risk of neural tube defects that leads to cleft palate.
Hyaluronan is a carbohydrate polymer found in connective tissue and hard palate. The HYAL2 gene encodes hyaluronidase 2, an enzyme responsible for degrading hyaluronan. An enzyme study by researchers revealed that mutations reduced levels of HYAL2 protein that inhibited metabolism of hyaluronan. It is found that mutations in genes HYAL2 cause cleft palate. Genetic changes causing these mutations occur due to mother's diet and certain medication during pregnancy. A baby born with a cleft palate have difficulties during speech, feeding, hearing and vision impairment.
What are the symptoms of cleft palate deformity?
Cleft palate is a split, a gap in the lip and roof of the mouth that affects one or both sides of the mouth that is visible and can be immediately identified at birth. It may sometimes appear as a small notch in the lip or extends from lip through upper lip, upper gum and palate into bottom of nose. It may even appear a a split only on the roof of mouth that does not affect facial appearance.
A child is not comfortable while speaking that often force him or her to speech through nasal passage. Difficult speech is a common problem with child born with cleft palate.
A child faces problems during feeding.
Food cannot be swallowed by the child and liquids or food come out of the nose.
Chronic ear infections are seen in children with cleft palate.
Development of teeth is delayed with formation of cleft palate. Dental problems common in child with cleft palate are fused teeth, missing teeth or formation of extra teeth behind normal ones.
Oral hygiene is very difficult to maintain in child born with cleft palate that increases formation of cavities in teeth.
A child may find difficulties while socializing that may affect his behaviour causing anxiety and depression or aggressive nature with delayed cognitive skills.
How is cleft palate deformity diagnosed?
An ultrasound is a diagnostic test that help to identify cleft palate during pregnancy. Sometimes it is unable to diagnose submucosal cleft palate under ultrasound, so a child is born with it as a birth defect.
An amniocentesis – a procedure to extract sample of amniotic fluid from uterus to perceive the genetic syndrome that child might have inherited that may have caused cleft palate deformity is also advised as a diagnostic test by the doctor.
What is the treatment for cleft palate? Or What is cleft palate repair?
The main aim of cleft palate treatment aims to improve childs ability to eat, speak, hear normally and achieve normal facial appearance. A team of doctors such as surgeons like plastic surgeon or ENTs who specialize in cleft palate repair, paediatric dentists, oral surgeons, nurses, speech therapists and genetic counselors work in the treatment of cleft palate repair surgery.
A cleft palate repair surgery is based on childs condition due to cleft palate. The extent of cleft palate determines the surgery that is scheduled in a hospital. The goal of the surgery is to close the open riof of the mouth. A general anesthesia is given to the child prior the surgery is performed. A cleft palate repair surgery can be done when the child is upto 12 months of age or earlier.
A parent is called before a week of a planned surgery to question and record child's current medical condition, allergies, past surgeries or illness, immunization and medicines. Medical history is of prime importance to understand before the surgery is scheduled by the doctor.
A child is breast fed before 4 or 6 hours before the surgery. He is allowed clear liquids like water, apple or grape juice before 2 hours of surgery. Any deviation in normal health of child, complete medical history is noted by the nurse while the child is under observation in hospital before the planned surgery. A physical examination, temperature and weight of child are recorded.
After giving general anesthesia to the child, an IV is put into the vein for stronger pain medication that puts child into a deep sleep. A plastic surgeon then conducts the surgery by following few steps. Majority of cleft palate repair surgeries done using two flap palatoplasty technique using bilateral palatal flaps to close the midline of roof of mouth.
Child's mouth is kept open through a device during the surgery. Incisions are made on both sides of the palate along the cleft. The layer of the tissue attached to the hard palate is made to loosen and stretch. A cut is made along the gums for tissues to move towards the middle of the roof of the mouth. The inner nasal layer of tissues is closed using sutures that dissolves as the incision heals. The outer oral layer of tissue is closed by through sutures that eventually dissolves. These incisions that are meant to close the roof of mouth form a Z shape appearance. This surgery places the muscles of the soft palate in normal position that helps in normal functions of speech and swallowing food. The child is allowed to go home after 3 days of stay in hospital post surgery. A child is prescribed analgesic and antibiotic for few days. It is important for child to drink fluids to prevent dehydration. The upper jaw that have caused cleft palate is now repaired along with repair of cleft of the gum by expert surgeons.
An orthodontist then repositions the teeth. A speech therapist helps the child to develop normal speech and solves eating issues. A clinical psychologist helps the child to cope up with different behavioral problems and cognitive skills. An ENT helps to cope up with hearing.
Prevention of birth defects like cleft palate can be done through a healthy lifestyle, eating nutritious food during pregnancy. Avoid alcohol consumption, smoking and unnecessary medications during pregnancy.
cleft palate child suregry
No Comments